Clinical Image
Super Scan in Metastatic Extramammary Paget’s Disease
Yuka Uema1,2, Nao Kusutani2* and Daisuke Tsuruta2
1Department of Dermatology, Kashiwara Municipal Hospital, Japan
2Department of Dermatology, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan
*Corresponding author: Nao Kusutani, Department of Dermatology, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka, Japan
Published: 11 Jun, 2018
Cite this article as: Uema Y, Kusutani N and Tsuruta
D. Super Scan in Metastatic Extra
mammary Paget’s Disease. Clin
Oncol. 2018; 3: 1473.
Keywords
Bone metastases; Extra mammary Paget’s disease; Super scan
Clinical Image
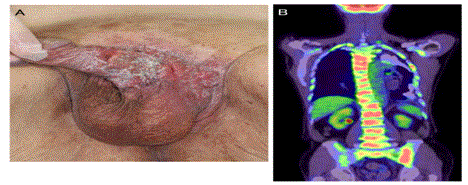
An 87-year-old Japanese man presented with severe chest pain, lower back pain, anorexia, and malaise. He had a surgical history of Extramammary Paget’s Disease (EMPD) of the penis and scrotum (Figure A). Fluorodeoxyglucose-Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography (FDG-PET/CT) revealed multiple bone lesions with FDG uptake, including the vertebrae, bilateral ribs, scapulae, the sternum, the pelvis, and the right femur, the so called “super scan” (Figure B). The super scan phenomenon is characterized by intense activity in the bones and diminished activity in the soft tissue and in renal parenchyma in bone scintigraphy; it is commonly observed in prostatic or breast cancer [1]. In this case, super scan on FDG-PET/CT was caused by EMPD, a cutaneous malignancy of apocrine sweat gland origin. EMPD commonly metastasizes to the regional lymph nodes, the liver, the lungs, and the bones, and the diagnosis of bone metastases was made with the help of FDG-PET/CT [2].
Figure A and B
References
- Osmond JD 3rd, Pendergrass HP, Potsaid MS. Accuracy of 99mTC-diphosphonate bone scans and roentgenograms in the detection of prostate, breast and lung carcinoma metastases. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1975;125:972-77.
- Fukuda K, Funakoshi T. Metastatic Extra mammary Paget's disease: Pathogenesis and Novel Therapeutic Approach. Front Oncol. 2018;8:38.